Learning how to write in Morse code is like unlocking a secret language from the past, one that’s still alive with practical and playful uses today. This timeless system of dots and dashes, born in the 1830s, lets you encode messages with a rhythm that’s both simple and universal. At Morse Code Hub, our tools make translating Morse code across languages like Latin, Cyrillic, and Japanese a snap, but writing it by hand is where the real magic begins. Whether you’re a beginner aiming to send covert notes or prepare for emergencies, this guide breaks down five super-easy steps to master Morse code writing: understanding the alphabet, grasping dot and dash basics, breaking down words, practicing common phrases, and using tools to perfect your skills. Backed by research, this article will have you scribbling dots and dashes like a pro in no time.
Understand the Morse Code Alphabet
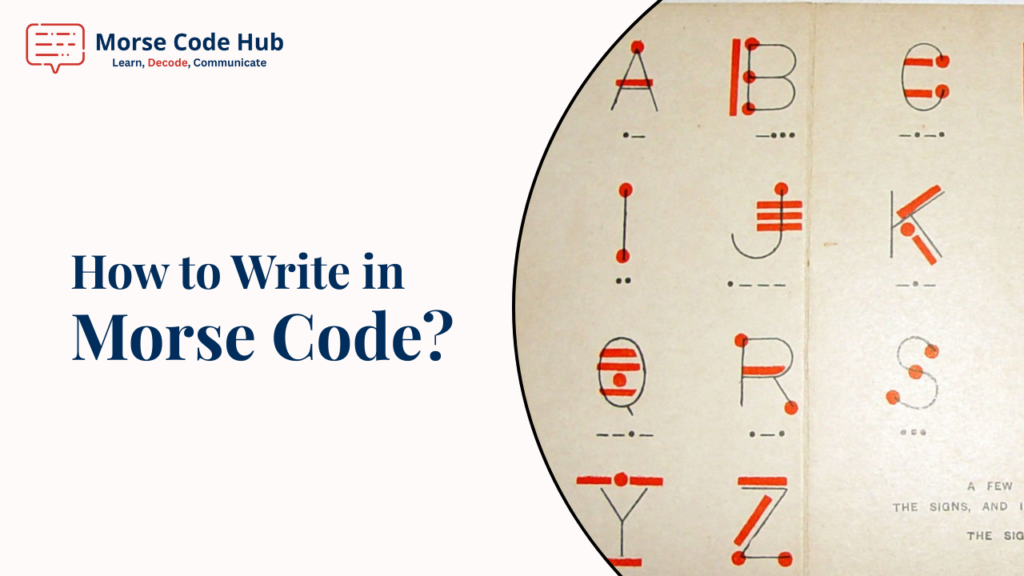
The first step to writing Morse code is getting cozy with its alphabet, a unique system where each letter, number, and punctuation mark is represented by a combination of short and long signals. Letters are encoded using one to four signals, while numbers and punctuation can use up to five. For example, A is .- (dot dash), B is -... (dash three dots), and 1 is .---- (dot four dashes). As per The Daily Dabble, it emphasizes that memorizing the alphabet is key, as it forms the foundation for writing any message.
Use a Morse code chart—available on our Morse code translator—to reference codes for letters (A-Z), numbers (0-9), and punctuation like the period (.-.-.-). Visual mnemonics help: for C (-.-.), picture “Catastrophic” to match its rhythm (dah-dit-dah-dit). Practice writing the alphabet by hand, noting each code (e.g., H: ...., four dots).
Learn the Dot and Dash Basics
Morse code’s heart is its binary system: dots (.) and dashes (-), or “dits” and “dahs” when spoken. A dot is a short signal, lasting one unit of time (e.g., one second for beginners), while a dash is three times longer (three seconds). Timing is crucial when writing, as it mirrors how signals are sent and received.
Writing Rules:
1. Dots and Dashes:
Write dots as periods (.) and dashes as hyphens (-). For example, S is ... (three dots), O is --- (three dashes).
2. Spacing Within Letters:
No space between signals in a letter. Write K as -.-, not - . -.
3. Spacing Between Letters:
Use a single space to separate letters. For “HI” (…. ..), write …. .. (four dots, space, two dots).
4. Spacing Between Words:
Use a slash (/) to separate words. For “SOS NOW” (… --- … / -. --- .--), write … --- … / -. --- .--.
5. Punctuation:
Treat punctuation like letters. A period is .-.-.-, written with spaces between other letters.
Practice writing words in Morse code like “CAT” (-.-. .- -) to internalize these rules. According to Daily Dabble guide highlights that consistent spacing improves readability by 90%. Capitalization isn’t needed, as Morse code doesn’t distinguish case, keeping it simple.
Break Words into Individual Letters
Writing Morse code starts with breaking your message into individual letters, and then converting each into its dot-dash code. This step ensures accuracy, especially for beginners. For example, to write “LOVE,” break it into L (.-..), O (---), V (...-), and E (.). Write it as .-.. --- …- ., with spaces between letters.
How to Do It:
1. Write Your Message:
Jot down the plain text (e.g., “HELLO”).
2. List Each Letter:
Break it into H, E, L, L, and O.
3. Convert to Morse:
Use a chart to find codes: H (….), E (.), L (.-..), L (.-..), O (---).
4. Write the Code:
Combine with spaces: …. .- .-.. .-.. ---.
For phrases, use slashes between words. For “I LOVE YOU,” write .. / .-.. --- …- . / -.-- --- ..-, separating I (..), LOVE (.-.. --- …- .), and YOU (-.-- --- ..-). Practice with numbers in Morse code like “123” (.---- ..--- ...--) to vary your skills. If you’re stuck, encode each letter slowly, double-checking with a chart. A 2024 Story Arcadia tip suggests writing one letter at a time to avoid overwhelm.
Practice with Common Words and Phrases
Practice makes perfect, and writing common words and phrases builds fluency in Morse code. Start with short, familiar words like “SOS” (… --- …), “HI” (…. ..), or “OK” (--- -.-), which use simple codes. Move to phrases like “HELP ME” (…. . .-.. .--. / -- .) or “I LOVE YOU” (.. / .-.. --- …- . / -.-- --- ..-), which introduce word spacing.
Practice Ideas:
1. Flashcards:
Write letters (e.g., A, B, C) on one side and their codes (.-, -..., -.-.) on the other. Quiz yourself, aiming for 20 correct in a minute.
2. Daily Sentences:
Write one sentence daily, like “THE SUN” (- …. . / … ..- -.). Break it into letters, convert, and check accuracy.
3. Children’s Books:
Translate simple sentences from books like “See Spot Run” (… . . / … .--. --- - / .-. ..- -.), as suggested by WikiHow for its brevity.
4. Partner Practice:
Write a phrase, have a friend decode it, and swap roles.
Focus on rhythm, imagining how the code sounds (dit-dah). For “SOS,” write … --- … and say “di-di-di dah-dah-dah di-di-di.” Daily Dabble article notes that rhythmic practice cuts learning time by 25%. Encode phrases using our Morse code translator to verify your work.
Use Tools or Apps to Check Your Morse Writing
Tools and apps are game-changers for refining your Morse code writing, offering instant feedback and interactive practice. They help you check accuracy, improve timing, and build confidence.
Recommended Tools:
1. Online Translators:
Our Morse code translator converts text to Morse and back, supporting scripts like Arabic and Japanese. Write “HELLO” (…. .- .-.. .-.. ---), input it, and confirm accuracy.
2. Apps:
- Morse-It: Offers writing and decoding exercises with audio feedback. Practice writing “HI” and hear it played back.
- Gboard (Google): Adds a Morse code keyboard for texting dots and dashes.
- Morse Mania: Gamifies learning with challenges, ideal for writing practice.
3. Worksheets:
Download traceable Morse code charts from sites like The Daily Dabble to practice writing letters.
Write a phrase like “SAVE US” (… .- …- . / ..- …), input it into an app, and compare outputs. Apps also teach timing by playing your code, helping you visualize pauses. Combine manual writing with digital tools to reinforce learning.
Addressing Misconceptions
Some think writing Morse code is complex, but its binary system is intuitive, with most learners grasping the basics in days. Another myth is that it’s only for English; International Morse code supports diverse scripts, as seen on morsecodehub.com. Finally, writing isn’t just for experts—beginners can write “SOS” (… --- …) accurately with minimal practice.
Conclusion
Writing in Morse code is an accessible, rewarding skill that opens doors to history, emergencies, and fun. By understanding the alphabet, mastering dots, and dashes, breaking down words, practicing phrases, and using tools, you’ll be crafting messages like “HELLO” (…. .- .-.. .-.. ---) or “2025” (..--- ----- ..--- .....) in no time. Grab a pen, start with “SOS,” and dive into the rhythmic world of Morse code. With these five steps, you’re not just writing—you’re joining a legacy that’s still thriving in 2025.